How to Use HighLevel Conversation AI Public APIs: Create, Manage, and Debug Agents
Master HighLevel’s Conversation AI public APIs to automate agent provisioning and custom booking actions. This guide for developers and agencies covers scaling personalized AI assistants, debugging reasoning, and optimizing CRM workflows across sub-accounts.

This guide explains how to use HighLevel's Conversation AI public APIs to build, configure, and operate conversational agents at scale. It covers core concepts, required permissions, common REST calls, example payloads, debugging tips, and real-world implementation patterns for agencies and SaaS teams using GHL for CRM, automations, and voice AI integrations.
Who this is for and why it matters
The Conversation AI public APIs are intended for developers, agencies, and platform operators who want programmatic control over conversational agents in HighLevel. Use cases include:
- Automated agent provisioning when a new client signs up or pays.
- Custom integrations that attach booking, handover, or workflow triggers to agents.
- Operational automation for bulk updates, audits, or cleanup across many sub-accounts.
- Debugging AI behavior by reading generation details and data sources used for responses.
Key concepts: agents, actions, and generations
Understanding three concepts simplifies working with the API:
- Agent — A conversational agent instance with settings like personality, goals, mode (suggestive vs autopilot), and channel configuration.
- Action — A discrete capability attached to an agent, such as appointment booking, requesting contact info, transferring to human, triggering a workflow, or scheduling follow-ups.
- Generation — A single AI response event; generation details include the chat history, reasoning, and the knowledge sources the agent used to craft that response.
Before you begin: prerequisites and permissions
Prepare the following before calling Conversation AI APIs:
- Active HighLevel account with API access.
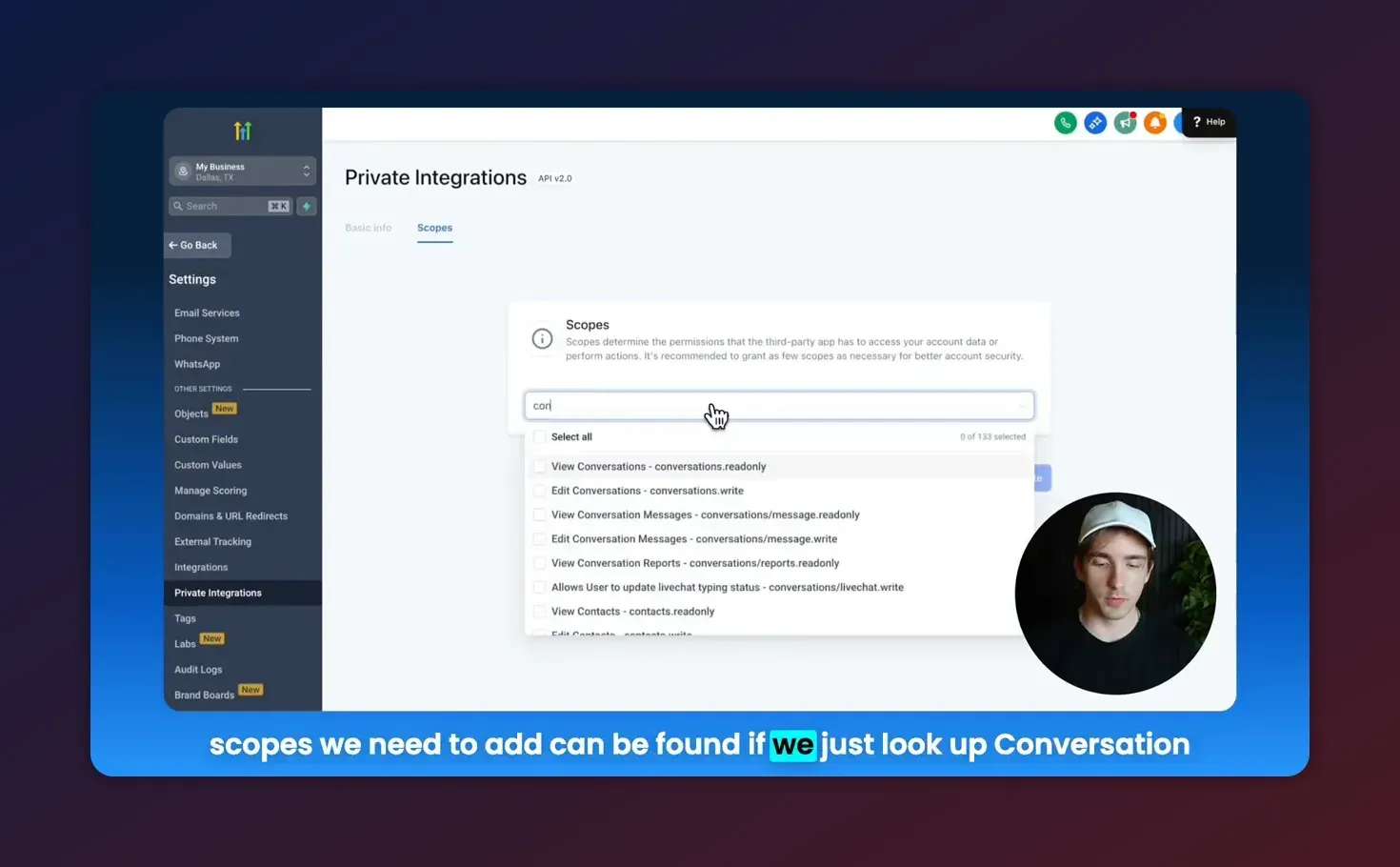
- Create a Private Integration in Settings > Private Integrations. Generate an API token for programmatic access.
- Grant the token the conversation AI scopes required for your operations. At minimum you will need read and write scopes for conversation AI so you can list and modify agents and actions.
- A test sub-account or staging environment for experimenting before production changes.
Quick API workflow: common tasks and sequence
Here is the typical sequence when automating a conversation AI flow:
- Authenticate with the Private Integration token.
- Create an agent programmatically or locate an existing one using search/get.
- Attach actions to the agent (booking, contact collection, transfer, follow-ups, workflow triggers).
- Update action configuration as required (trigger messages, workflow IDs, fields to collect).
- Read generation details to debug or audit AI responses.
- Optionally delete or disable agents when no longer needed.
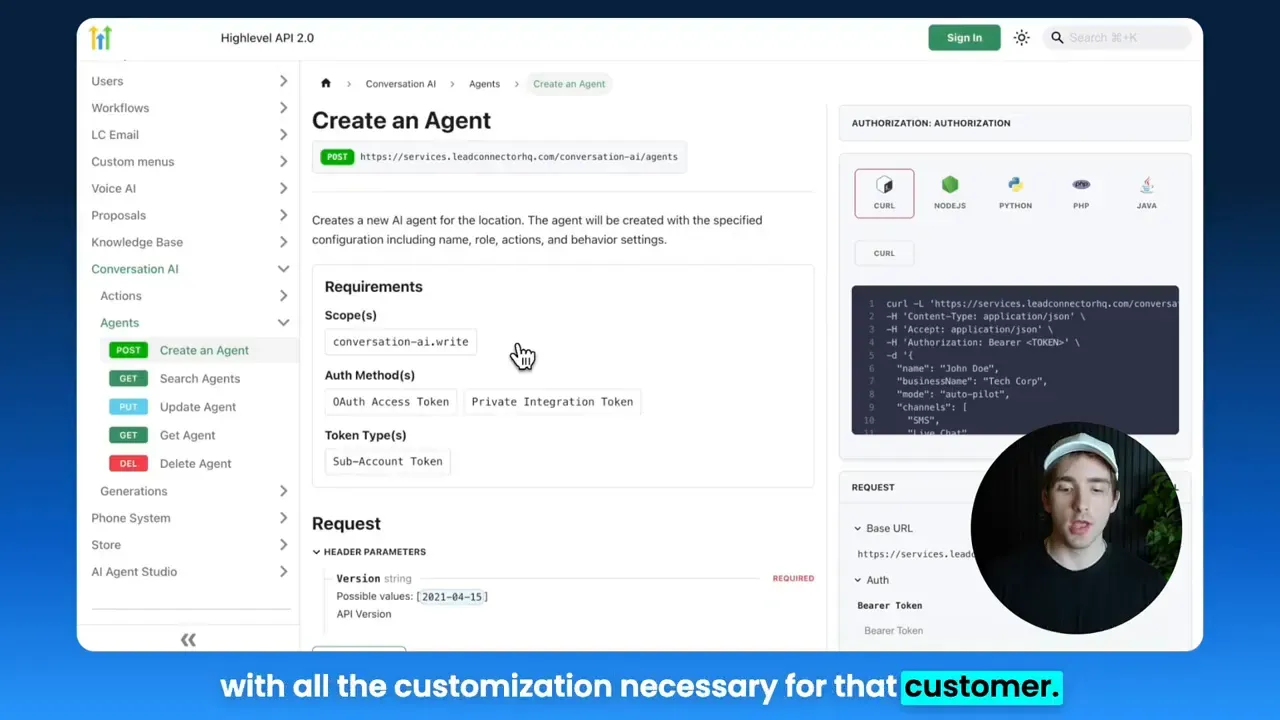
How to create an agent (example)
Creating an agent programmatically allows you to provision customized assistants for each customer or sub-account. A typical payload includes the agent name, business name, mode, channels, personality, goals, and initial actions or prompts.
curl -X POST "https://api.gohighlevel.com/v2/conversation/agents" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_PRIVATE_INTEGRATION_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"name": "Acme Support Agent",
"businessName": "Acme, Inc.",
"mode": "autopilot",
"channels": ["webchat", "sms"],
"isPrimary": true,
"personality": {
"tone": "friendly",
"greeting": "Hi! How can I help you today?"
},
"goal": "Book appointments and collect contact info"
}'Response will include an agentId. Save that ID — it is required for attaching actions or making updates.
Search, get, update, and delete agents
Use search to filter agents by name, status, or configuration. Use get to retrieve a single agent and its id. Use update to change settings and delete to remove an agent.
- Search agents — filter by status (active, inactive), mode (autopilot, suggestive), or partial name.
- Get agent — returns the full configuration including attached actions, prompts, and IDs.
- Update agent — modify anything supplied at creation (channels, prompts, goals, personality).
- Delete agent — removes the agent; consider soft-delete policies in your business before automating deletes.
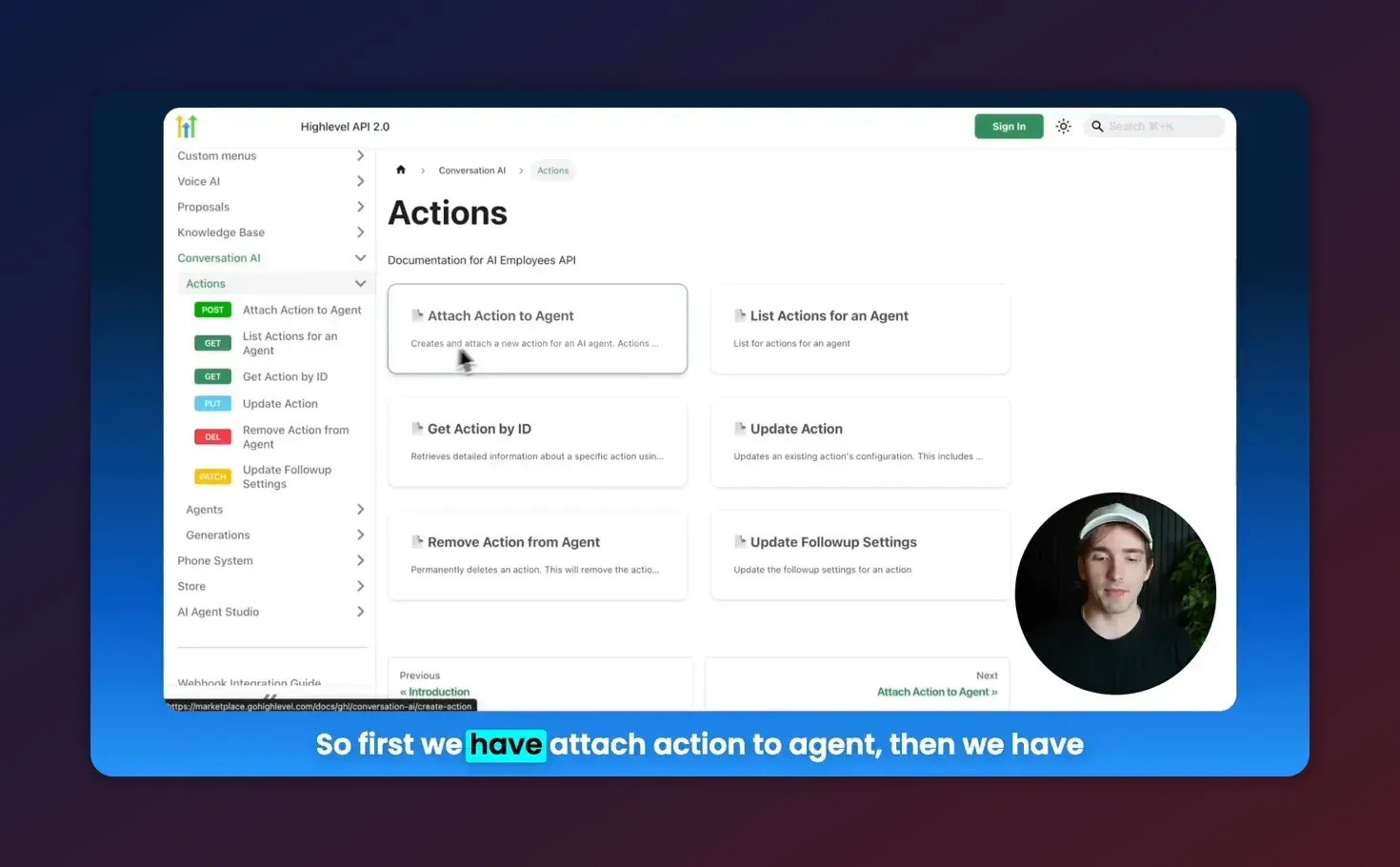
Actions: attach, list, update, remove
Actions grant actionable capabilities to agents. Typical action types:
- Appointment booking — lets the agent schedule leads into calendars.
- Collect contact info — prompts and captures phone, email, or custom fields.
- Trigger workflow — invokes HighLevel workflows and automations.
- Human handover / transfer — escalates to live agents.
- Auto follow-up — schedules follow-up interactions based on rules.
- Stop bot — stops automation and sets status to manual handling.
Attach an action to an agent (example)
curl -X POST "https://api.gohighlevel.com/v2/conversation/agents/{agentId}/actions" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_PRIVATE_INTEGRATION_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"type": "appointmentBooking",
"name": "Book Demo",
"settings": {
"calendarId": "cal_123",
"availableTimes": ["9:00","10:00","14:00"],
"confirmationMessage": "Appointment confirmed for {date} at {time}"
}
}'To find action IDs later, call the list actions endpoint for that agent. That response returns each action with its unique actionId.
Update or remove an action
Use the actionId to change configuration (trigger messages, workflow IDs, contact fields) or to remove the action from the agent.
curl -X PATCH "https://api.gohighlevel.com/v2/conversation/agents/{agentId}/actions/{actionId}" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_PRIVATE_INTEGRATION_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"name": "Book Initial Demo",
"settings": {
"availableTimes": ["11:00","13:00"],
"workflowOnConfirm": "workflow_456"
}
}'Generation details: how to read what the AI used
Generation details are essential for auditing and debugging agent responses. They reveal:
- Which pieces of the conversation history were used to produce a reply.
- Which knowledge sources were referenced (knowledge base articles, FAQs, external web content, or tables).
- Why the agent selected a particular answer or action.
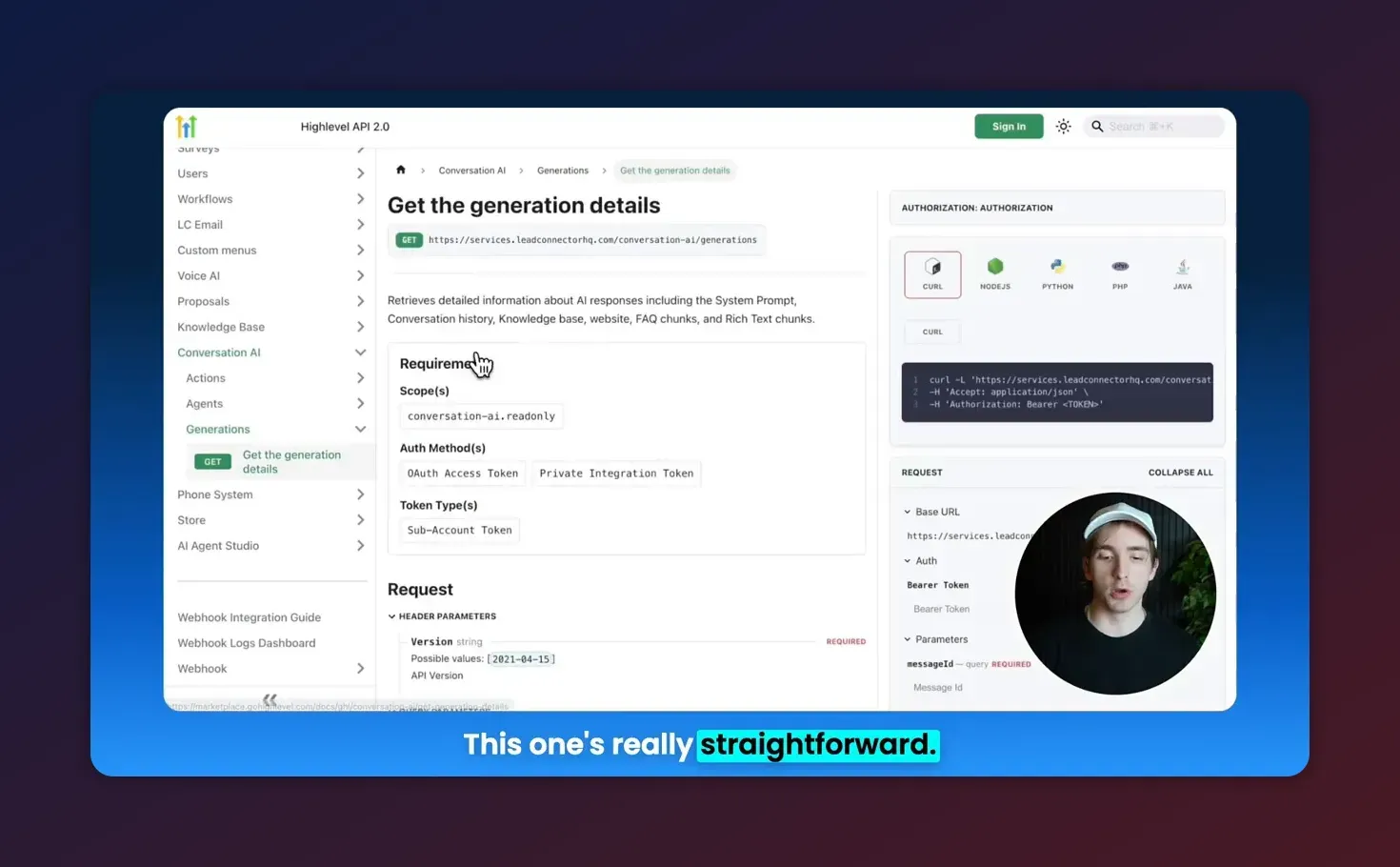
Typical usage: when a user receives an unexpected response, fetch generation details for the message to see the evidence chain. This helps identify stale knowledge bases, incorrect embeddings, or improper action triggers.
Implementation patterns and examples
Automated provisioning per customer
Integrate agent creation into your onboarding workflow:
- Customer pays or completes signup.
- Your backend calls Create Agent using a template payload (personality, goals, channels).
- Your system attaches standard actions: contact collection, appointment booking, and a workflow trigger to kick off onboarding automations.
- Save agentId and actionIds in your CRM for future updates or analytics.
Bulk updates and staff onboarding
Use search agents to return a list of internal agents and then run update operations to add new knowledge base entries or change prompts when a staff member joins or processes change.
Start Your HighLevel Trial + Get Instant Nexus Hub Access
Build, scale, and optimize your business with HighLevel. Start a free trial using this link to get automatic access to the Nexus Hub community, templates, and implementation resources.
Start Free TrialCombine with other HighLevel features
The Conversation AI APIs work well with other HighLevel components:
- Workflows and automations — trigger automations when an action fires.
- Knowledge bases — keep content updated to ensure accurate AI answers.
- Voice AI — route phone interactions to the same agent logic for consistent behavior across channels.
- CRM — persist leads and field captures directly into HighLevel contact records.
Pitfalls, limitations, and best practices
When working with Conversation AI APIs, watch for these common issues:
- Incorrect scopes: Missing read or write conversation AI scopes will cause 401 or permission errors. Verify the Private Integration token scopes include both read and write where you expect to modify resources.
- ID management: Store agentId and actionId reliably. Many operations require both agent and action IDs, so persisting them prevents extra API calls.
- Rate limits: Plan for API rate limiting. Batch updates into sensible windows and implement retries with exponential backoff.
- Destructive operations: Deleting agents is irreversible in many systems. Add confirmation steps, soft-delete flags, or retention policies before bulk deletes.
- Follow-up complexity: Follow-up rules can be complex. Test follow-up settings in a staging environment before enabling them for live users.
- Knowledge drift: Keep knowledge bases and FAQs updated. Generation details will help identify outdated referenced material.
Checklist for a safe rollout
- Set up Private Integration and verify conversation AI scopes.
- Test create agent flow in a sandbox account.
- Attach minimal actions first (contact capture) before enabling booking or transfers.
- Enable logging and store generation details for early conversations.
- Monitor for unexpected behavior and iterate on agent prompts and knowledge base content.
Example: create agent on payment event (workflow)
A common automation is to provision an agent right after a successful payment. The high-level steps:
- Payment completes in your billing system.
- Your backend receives webhook and validates payment.
- Backend calls Create Agent API with a template adapted to the customer's settings.
- Attach required actions (booking, contact capture, onboarding workflow trigger).
- Send a welcome message and schedule a follow-up via HighLevel workflow.
Troubleshooting tips
- If an API call fails, first verify the token header and scopes, then check the request body for required fields.
- Use get agent and list actions to confirm objects were created and to retrieve their IDs.
- When debugging unexpected AI responses, fetch generation details to see which knowledge sources and conversation history were considered.
- Keep a staging account to test changes to agent prompts, actions, and follow-ups before applying them to production customers.
Performance and scale considerations
When creating thousands of agents or orchestrating large updates:
- Design idempotent provisioning logic to avoid duplicate agents on retries.
- Use bulk or batched jobs during off-peak hours where possible.
- Monitor API quotas and implement client-side throttling.
- Cache agent metadata to reduce repeated calls to search/get endpoints.
- Centralize templates for agents and actions so updates can be applied cleanly across many agents.
Resources and next steps
To go further:
- Review the official HighLevel API documentation for exact endpoint paths, required fields, and response shapes.
- Set up a Private Integration token and test calls against a staging sub-account.
- Start with a single automated provisioning pipeline, then iterate toward bulk provisioning and lifecycle management.
- Consider joining the Nexus Hub community for templates, agent prompts, and implementation support.
Summary
HighLevel's Conversation AI public APIs enable full programmatic control over agents, actions, and generation data. With proper token scopes and tested templates, agencies and SaaS operators can provision agents per customer, attach booking and workflow capabilities, and inspect generation details to debug AI behavior. Follow safe rollout practices, store agent and action IDs, and combine conversation AI with workflows, knowledge bases, and voice AI to build consistent omni-channel experiences.
Frequently asked questions
How do I get the API token and what scopes are required?
Create a Private Integration in HighLevel settings. Generate an API token and ensure it includes conversation AI read and write scopes so the token can list, create, and modify agents and actions.
What is the difference between an agent and an action?
An agent is the conversational entity (personality, goals, channels). Actions are capabilities attached to agents, like booking appointments, collecting contact fields, transferring to humans, or triggering workflows.
How can I debug why an agent produced a specific response?
Use the generation details API to retrieve the chat history, the reasoning for the response, and the knowledge sources consulted. This helps identify if the agent referenced an outdated FAQ or misapplied a rule.
Is it safe to automate deleting agents?
Deleting agents can be destructive. Implement soft-delete patterns, confirmations, or retention windows. For automated cleanup, log deletions and provide an undo window if your workflow allows.
Can I integrate Conversation AI with HighLevel workflows and voice AI?
Yes. Attach action triggers that call workflows and route voice interactions to the same agent logic. This keeps chat and voice responses consistent and allows CRM updates and automations to run in response to agent events.
Ready to try this in your account?
If you do not yet have a HighLevel account, consider starting a free trial to test Conversation AI flows end-to-end. For agencies seeking templates, community support, and implementation help, Nexus Hub is a useful resource for prebuilt agent templates and automations.
Start Your HighLevel Trial + Get Instant Nexus Hub Access
Build, scale, and optimize your business with HighLevel. Start a free trial using this link to get automatic access to the Nexus Hub community, templates, and implementation resources.
Start Free Trial